
Understanding eUICC & Remote SIM Provisioning
Changing connectivity providers used to require physically switching SIM cards. With a single device, this is quite easy, but changing a large number of SIM cards physically would be too costly for an IoT solution provider, especially if the devices are deployed all around the world. With Remote SIM Provisioning, enterprises can remotely switch the principal cellular carrier of their devices, which is a major game-changer for cellular IoT. Here’s everything you need to understand to make your IoT more efficient and eUICC compatible.
What is eUICC?
Dubbed the next generation of SIM cards, the eUICC (Embedded Universal Integrated Circuit Card) allows consumers to switch service providers over-the-air (OTA) without having to physically replace the embedded SIM card. eUICC is the most significant development in more than 20 years that GSM connectivity has existed. It offers the ability of to choose and modify connectivity provider credentials.
What is Remote SIM Provisioning (RSP)?
The technique of remotely controlling SIM profiles in IoT devices is known as Remote SIM Provisioning. The GSMA RSP specifications outline the proper procedure for remote Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) programming and activation. Numerous activities involved in the lifecycle of a mobile service or M2M service are intended to be made simpler by this specification. Additionally, it develops new business models in which a single customer may have several operators (profiles kept in the eSIM) for various services such as roaming, data service, etc. Remote SIM provisioning is enabled by an eUICC, a technology that is part of the embedded SIM (eSIM) standard and is commonly confused with an eSIM.
Who benefits from remote SIM provisioning?
By bridging the gap between IoT devices and the digital world, SIM provisioning can lead to a multitude of opportunities when combined with eUICC. Almost all industries employ remote SIM provisioning. There are numerous developments centered around the remote provisioning of SIM cards, ranging from energy to agriculture.
For example, consider a smart waste management company that equips its cluster of cellular-connected smart bins with a single SIM card. Following production and allocation, the smart dustbins are given the appropriate cellular profile for their intended location and the cluster is ready for global shipping. Even after an end-user activates the smart bin, the company can continue to access the smart devices remotely to ensure connectivity and finish important upgrades.
In another scenario consider deploying thousands of devices with the same supplier SIM cards and MNO profiles across different nations. Then your carrier files for bankruptcy or goes out of business. Alternatively, it's possible that they have chosen to transfer bandwidth from the necessary network (like 2G or 3G) to more recent cellular technologies (like 4G or 5G). You must reprovision your devices with new SIM profiles prior to the carrier shutting down the network in order to preserve service. That's not a problem with remote SIM provisioning; you can locate another provider that has coverage in the same area. However, all those SIMs need to be physically replaced if eUICC is not available.
It costs money to manually replace SIMs. In addition to buying thousands of extra SIM cards, you also need to dispatch field representatives to your device locations to manually install them in order to guarantee proper functionality and prevent your clients from bearing the entire cost of this exercise. Your customers will also pay a high price for it because installing the new SIMs will probably require a lot of downtime. They lose out on business from that disturbance, even if it is planned.
Hence, remote SIM provisioning is crucial for IoT enterprises' scalability and long-term success. It lets you give your customers future-proof cellular access while cutting costs and deployment times. You can reach out to our experts to understand how it can help your business.
Types of RSP - consumer eSIM vs M2M eSIM
According to GSMA, RSP provides two distinct architectures. Consumer devices are the focus of one, whereas M2M is the focus of the other.
RSP for M2M

RSP for M2M was the initial solution created, mostly due to the rapidly expanding market demands. This architecture can be divided into three basic elements:
RSP for Consumer
Due to the numerous extra use cases that arise from end-user contact, the solution for consumer devices is more complicated. It is possible to identify four key components in this architecture:
- Subscription Manager (Data Preparation +, or SM-DP+) - As demonstrated by the M2M solution, SM-DP+ takes on both SM-DP and SM-SR duties. Thus, in addition to creating, downloading, and managing profiles, it also provides the necessary operator credential protection.
- Subscription Manager (Discovery Server, or SM-DS) - Regardless of the access network the device is linked to, SM-DS ensures that the SM-DP+ will reach the eUICC. Since devices can be connected via several access networks with various addresses, this feature is crucial. By enabling SMDP+ to publish alerts to a secure noticeboard and for devices to extract those alerts, the SM-DS solves this problem. When Profile data is available for download to the eUICC, it serves to alert the LPA.
- Local Profile Assistant, or LPA - For devices that use eSIM technology, LPA is a necessary component. It provides the option to download Profiles that are encrypted to the eUICC.
- Embedded universal integrated circuit cards, or eUICCs - The same function as that mentioned for M2M is provided by the eUICC.
People Also Ask - Difference between eUICC & eSIM
When one glances briefly at the RSP Architecture, one may mistakenly believe that eSIM and eUICC are the same thing. Nevertheless, those two ideas differ fundamentally from one another. Whereas eUICC is software, eSIM is hardware.
If you are looking for eUICC enabled SIM/ eSIM solutions, get in touch with sales@connectedyou.io. Our experts will help you out.
Why ConnectedYou?
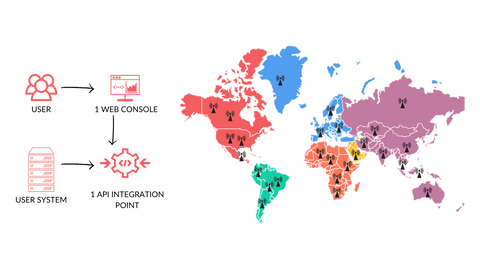
Our connectivity solution is universally independent of any connectivity provider. Choose from 40+ pre-integrated connectivity suppliers based on your connectivity requirements across different regions
We orchestrate the critical components that include - eUICC-enabled SIMs/ eSIMs, global IoT/ M2M connectivity, unified monitoring & management, and remote SIM provisioning capabilities into a single solution as a one-stop-shop. Here’s why our product is the best solution for your enterprise -
- The largest network of 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G, LTE-M, and NB-IoT networks
- Connectivity for countries with permanent roaming restrictions
- Transparent Pay-As-You-Go pricing without hidden charges or minimum commitments
- Single contract enabling hassle-free multi-supplier sourcing without lock-ins with any connectivity provider
- Unified platform to manage your IoT/ M2M SIM cards irrespective of the connectivity supplier
- Capability to switch connectivity suppliers remotely without SIM replacement and without any additional transaction costs
- Central support desk for all connectivity issues
Written by Neha Verma & Parag Mittal @ConnectedYou
